Imagine living in a house where you just need to turn on the heating in winter or air conditioning in summer. A house that practically heats up alone in the cold months and keeps you cool and comfortable during the summer, all of this without relying on large air conditioning systems conventional. This is not science fiction, but a tangible reality thanks to the passive houses .
In a world increasingly aware of the importance of sustainability and energy efficiency, passive houses are presented as an innovative solution and promising for the construction sector. These homes are designed to maximize comfort and minimize energy consumption, are revolutionizing the way in which we conceive and inhabit our homes.
In this comprehensive article, we explore in-depth the concept of passive house, its fundamental principles, advantages and the process of construction, providing a comprehensive guide for those interested in this approach avant-garde of the sustainable architecture.
In this post, we delve into:
What is a Passive House?
The concept of "passive house" was born in Germany in the 90's, when a group of scientists led by Wolfgang Feist developed the standard Passive House (or Passivhaus , in German). This standard not only seeks to drastically reduce the energy consumption of a house, but also improve the quality of life of its occupants through a clever design and the use of advanced technologies. In simple terms, a passive house is a home that manages to maintain a thermal comfort is optimal throughout the year, using very little energy.
But, why should we worry about building or buying a passive house? The answer is simple: we live in a world where the climate crisis and rising energy costs are problems with increasingly urgent. Passive houses offer a practical, sustainable solution that not only benefits the environment, but also our wallets.
To reduce the energy consumption, these homes save money in the long term, while they contribute to reducing our carbon footprint. In addition, they offer other important benefits, such as excellent indoor air quality and a healthy environment for its inhabitants.
In this article, we will explore in detail what makes the passive houses are so special. We will talk about the fundamental principles that define the materials used in its construction, air-conditioning systems that make them work, and much more. If you are interested in learning how you can take advantage of this innovative technology, we are still reading!
How does a Passive House?
The concept of passive house is based on the creation of an indoor environment comfortable without the need for conventional heating or cooling. This is achieved by careful planning and execution of various construction components and design techniques that work together to maintain an internal temperature stable and enjoyable during the whole year.
The basic principles of a passive house, which include:
- Thermal insulation, high-efficiency
- Windows and doors high performance
- Mechanical ventilation with recovery of heat
- Air tightness
- Orientation and passive solar design
To understand how passive houses, it is important to know the five basic principles that define them. These principles are the basis of the standard Passivhaus and ensure that a home is truly efficient. Below, we break down each one of them so that you can better understand how to work together to create a comfortable environment, and sustainable.
1. Thermal insulation: The Heart of a Passive House
The thermal insulation it is, without a doubt, one of the most important aspects of a passive house. It is the first step towards the creation of a barrier that minimises heat loss in winter and avoid summer heat. Without good insulation, any attempt to build a house passive would be destined for failure.
When we talk about thermal insulation, we refer to the ability of a material to prevent the heat from escaping or entering a home. In a passive house, the insulation must be extremely efficient, since that is the main responsible for maintaining a stable temperature within the housing. This means that the walls, ceilings and floors should be perfectly insulated to avoid what we call "thermal bridges", which are weak points where the heat can escape easily.
There are several types of insulating materials used in the construction of passive houses, and each one has its own advantages and disadvantages. For example, the rock wool it is a material derived from the volcanic stone that offers an excellent thermal and acoustic performance. In addition, it is fire-resistant and environmentally friendly, which makes it a popular choice. On the other hand, the cork it is a natural material and renewable energy that provides a great thermal and acoustic insulation. It is also waterproof and environmentally friendly, which makes it ideal for those looking for sustainable options.
Another common material is the cellulose , which is made from recycled paper. Cellulose is a material insulation is very efficient, which also helps to reduce waste, making it an eco-friendly choice. Finally, the expanded polystyrene (EPS) it is a synthetic material that is lightweight, inexpensive, and provides a good thermal performance, although it is not as eco-friendly as other materials mentioned above.
It is important to note that the thickness of the insulation varies according to the climate in which the building of the housing. In cold climates, the thickness of the insulation can exceed 30 cm, especially on the walls and the roofs, which are the areas most vulnerable to heat loss. In more temperate climates, such as the mediterranean, the thickness can be less, but it is still crucial to ensure a good energy performance.
A good insulation not only reduces energy consumption, but also improves the thermal comfort and acoustic housing. Imagine living in a house where the exterior noise can hardly be heard, and where the temperature is always pleasant, regardless of the external weather conditions. That is the magic of the thermal insulation in a passive house.
In addition, the thermal insulation has a positive impact on the health of the occupants. A good insulation keep cold draughts in winter, which can cause discomfort and increase the risk of respiratory diseases. It also helps to control the moisture inside the housing, preventing problems such as condensation, mold and mildew, which can negatively affect health.
In summary, the thermal insulation is the heart of a passive house. Not only ensures that the housing is efficient from the energy point of view, but also contributes to an environment more healthy and comfortable for their occupants.
2. Windows and Doors High Performance: Minimizing Heat Loss
The windows play a crucial role in the energy performance of a passive house. Not only are responsible for allowing the entrance of natural light, but you also need to minimize heat loss and maximize profits passive solar. To achieve this, the windows in a passive house are designed with specific features that make them very different from the windows of conventional.
One of the most outstanding features of the windows in a passive house is the use of glass double or triple glazing . The triple glazing it is the recommended standard, as it offers a superior thermal insulation than the double glazing. Between the crystals, using an inert gas such as argon or krypton, to further enhance the isolation. This gas acts as an additional barrier that reduces heat transfer between the interior and the exterior of the home.
In addition to the glazing, window frames are also important. The most common materials include wood , which provides excellent insulation and is a renewable material; the PVC , which is inexpensive, durable, and has good insulating properties; and aluminum with thermal break , which combines the strength of aluminum with a thermal insulation improved.
The orientation of the windows is another key aspect in the design of a passive house. In the northern hemisphere, the main windows should be oriented to the south to maximize solar gains in winter. During the cold winter months, the sun low on the horizon, and goes straight for the south-facing windows, heating the home, the natural way. However, in summer, the sun is higher in the sky and can get too hot if precautions are not taken. To avoid this, we use elements such as overhangs , awnings or even vegetation strategically placed to shade the windows.
In summary, the windows in a passive house are not just an aesthetic element, but they also play a fundamental role in the energy performance of the dwelling. Thanks to its intelligent design allow you to maximize solar gain in winter, while minimizing heat losses and the excess heat in the summer.
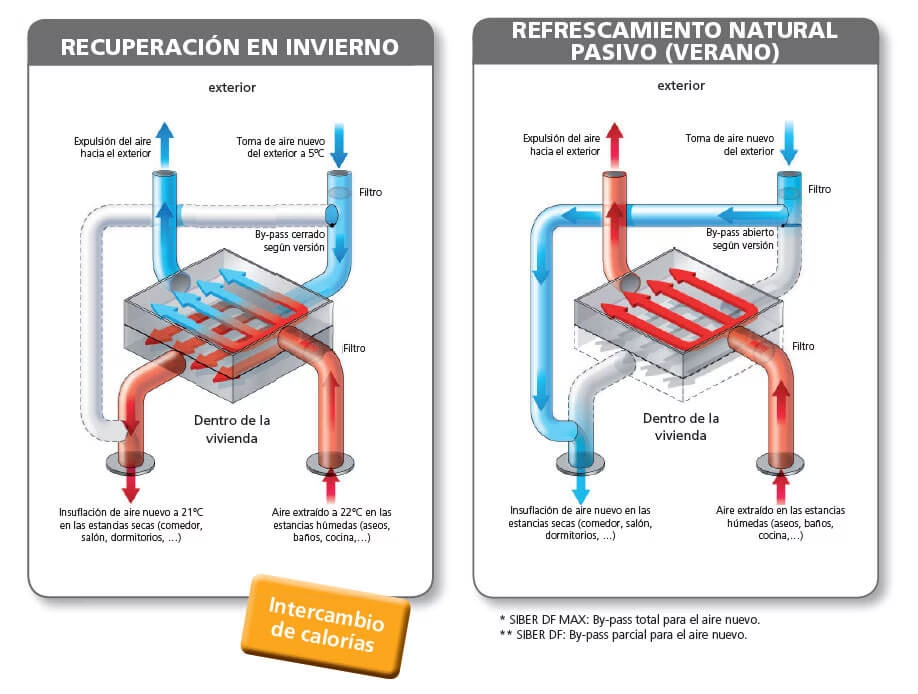
3. Controlled Mechanical ventilation (VMC): Renewing the Air without Losing Energy
One of the most innovative features of passive houses is the system of controlled mechanical ventilation (VMC) . This system is essential to ensure a constant flow of fresh air inside the home while the heat recovery of the exhaust air. In other words, it allows the indoor air is renewed without losing the energy that has already been used to heat or cool that air.
The operation of a system VMC is pretty ingenious. The stale air, which comes from areas such as kitchens and bathrooms, it is removed from the housing and passes through a recuperator heat . This device transfers heat from the exhaust air to the fresh air coming in, and that comes from the outside. The result is that the fresh air that enters the housing is already preheated, which significantly reduces the need to use heating systems additional. In some cases, the recovery of heat can reach efficiencies of up to 90%, which means that virtually no energy is lost in the process.
In addition to improving the air quality, the VMC also helps to control the humidity in the housing. An excess of moisture can lead to problems such as condensation, mold and mildew, which not only damage the structure of the home, but also can negatively affect the health of its occupants. With a system VMC appropriate, you can maintain a level of optimum moisture, which contributes to a healthier environment, and comfortable.
Systems VMC usually include air filters that remove particles, dust, pollen and other contaminants. This is especially beneficial for people with allergies or respiratory problems, because it ensures that the air you breathe is clean and pure.
In summary, controlled mechanical ventilation is an essential component of a passive house. It not only ensures that the indoor air is fresh and clean, but also contributes to the energy efficiency of the property to recover the heat from the stale air.
4. Air tightness: Avoiding Leakage of Heat and Air Currents
A passive house must be extremely tight to prevent air leaks. This means that all seams and joints, especially around windows, doors and ducts must be sealed carefully. The air tightness is crucial because, without it, the hot air can escape in the winter and cool air may enter the summer that would compromise the energy performance of the dwelling.
To make sure that a passive house compliant with the standards of water resistance, a test known as Blower Door Test . During this test, place a fan in the front door of the house to create a pressure difference between the inside and the outside. This allows it to detect any leakage of air, and corrected before the home is finished.
The air tightness not only improves energy efficiency, but also contributes to a better thermal comfort and acoustic. In a passive house properly sealed, there are no draughts or cold spots, which creates a more enjoyable environment for its occupants.
5. Use of Solar Energy: Solar Gains Passive
The design of a passive house takes maximum advantage solar energy to heat the home in winter. This is achieved through a proper guidance and the use of materials with high thermal mass , such as concrete or stone.
In the northern hemisphere, the main windows should be oriented to the south to maximize solar gains in winter. During the cold winter months, the sun low on the horizon, and goes straight for the south-facing windows, heating the home, the natural way. However, in summer, the sun is higher in the sky and can get too hot if precautions are not taken. To avoid this, we use elements such as overhangs , awnings or even vegetation strategically placed to shade the windows.
Materials with high thermal mass, such as concrete or stone, they absorb the heat during the day and release it slowly during the night. This helps to maintain a stable temperature within the housing, which contributes to the thermal comfort.
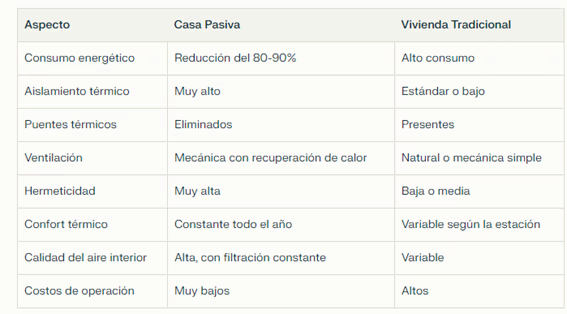
Comparison of a passive house with a traditional home
The differences between a passive house and a traditional home, are significant:
Benefits to the environment and health
Passive houses offer numerous benefits to both the environment and the health of its occupants:
- Significant reduction of CO2 emissions
- Less consumption of natural resources
- Improvement of indoor air quality
- Removal of mold and humidity problems
- Reduction of allergies and respiratory problems
- Increased acoustic comfort
Advantages of living in a Passive House
Live in a passive house offers numerous advantages that go beyond energy savings. These homes provide a level of comfort and quality of life superior to that of the conventional buildings.
Energy Saving Is Significant
One of the biggest advantages of passive houses is its ability to drastically reduce the energy consumption. Thanks to its intelligent design, and the use of advanced technologies, these homes can save up to 90% of the energy used for heating and cooling in comparison with a conventional home. This not only reduces energy bills, but also contributes to a lower environmental impact.
Thermal Comfort Constant
Passive houses are designed to maintain a constant temperature throughout the year, regardless of the external weather conditions. This means that the occupants can enjoy a comfortable environment and pleasant without having to worry about setting a thermostat or turn on the air conditioning systems in conventional.
Improvement of Indoor Air Quality
The system of controlled mechanical ventilation (VMC) ensures that the air inside is fresh and clean at all times. Besides, the air filters remove particles, dust, pollen, and other pollutants, which is especially beneficial for people with allergies or respiratory problems.
Positive impact on the Environment
To reduce the consumption of energy and use sustainable materials, passive houses contribute to reduce the carbon footprint and promote a style of life more respectful with the environment. This is especially important in a world where the climate crisis is a growing concern.
Recovery of the housing
Invest in a passive house not only provides immediate benefits in terms of comfort and savings, but also increases the value of the property long-term. As the growing awareness about energy efficiency and sustainability, passive houses are becoming more and more attractive in the real estate market.
The certification Passivhausinternationally recognized, adds an additional value to the home, diferenciándola in the market and attract buyers aware of the environment and energy efficiency.
Disadvantages of living in a Passive House
High Initial Cost
Although passive houses offer significant savings in the long term, the initial cost of construction is usually a 10-15% higher than a conventional home. This is mainly due to the use of high quality materials, advanced systems of air-conditioning and ventilation, and the need of a meticulous design.
It Requires Meticulous Planning
Build a passive house is not as simple as building a conventional home. It requires careful planning and a detailed design to ensure that all the elements work together efficiently. In addition, it is important to work with experienced professionals in the standard Passivhaus to avoid costly mistakes.
Limitations in the renovation of Existing Housing stock
Although it is possible to convert an existing house in a passive house, the process can be complicated and costly. In many cases, it would be necessary to make significant structural changes, such as improving the thermal insulation, replacing windows and doors, and install a system of controlled mechanical ventilation. This can make the reform is not feasible in some cases.
Heating and Cooling systems in Passive Houses
Although a passive house minimizes the need for conventional heating and cooling, it still requires complementary solutions to maintain the thermal comfort. In this section, we will explore some of the most common options and efficient.
Aerothermal: The Most Common and Efficient
The aerothermal it is a technology that has gained popularity in recent years due to their energy efficiency and their ability to adapt to different climates. In a passive house, where the energy consumption should be kept to a minimum, the aerothermal becomes an ideal solution because it uses the energy of the outside air to heat or cool the home. But, how exactly does this system?
Heat pumps aerotérmicas work by transferring heat from the outside air to the interior of the home in winter, and vice versa in summer. This process is based on a thermodynamic cycle that uses a compressor and a refrigerant to extract heat energy from the air, even when outside temperatures are low. Although it may seem surprising, these pumps can extract heat from the air even when the temperatures are below 0°C, although its efficiency decreases slightly in extremely cold conditions.
One of the great advantages of the aerothermal is its versatility. In addition to providing heating in the winter, it can be used to cool the home in summer, which makes it an integral solution for the climate control. In addition, heat pumps aerotérmicas are usually designed to work in combination with other systems, such as the underfloor heating or fan convectors , which allows to distribute the heat or cold evenly throughout the home.
The underfloor heating it is an option especially interesting in passive houses because it distributes the heat evenly from the ground up, creating a warm and comfortable without the need to resort to conventional radiator. On the other hand, the fan convectors are compact units that function as ventilators that emit hot or cold air, depending on the season. They are ideal for smaller spaces or where the floor heating is not feasible.
It is important to note that, although the aerothermal is an advanced technology, its installation is not overly complex. However, it requires careful design to ensure that the system functions optimally. In addition, it is essential that the property already has a good thermal insulation, as the aerothermal is designed to work in environments that are highly efficient, such as passive houses.
Thermal Solar panels for Hot Water
Another common alternative in the passive houses are solar panels thermal , which are mainly used for heating sanitary water. This system uses the sun's energy to heat a fluid that circulates through the panels and transfers the heat to the water stored in a tank. It is a solution for sustainable and efficient, especially in regions with abundant sunlight.
Solar panels are an excellent choice to supplement the heating system and further reduce the energy consumption of a passive house. In addition, they are relatively easy to install and have a long service life, which makes it a profitable investment in the long term. However, it is important to note that its performance depends largely on the amount of sun hours available, so in temperate climates may require a system of additional support.
Wood burning stoves: As a Support, Not the Main Source
In very cold climates, some houses passive incorporate wood burning stoves as a support system to heat the home during the months are more rigorous. However, it is crucial to understand that the wood stoves should not be the main source of heating in a passive house. Their use should be limited to specific situations, such as emissions of CO2 and can affect the indoor air quality if not treated properly.
In addition, the wood-burning stoves must be designed to be highly efficient and should be integrated in the overall design of the housing to minimize their environmental impact. Some modern include stoves with combustion systems clean that significantly reduce emissions and maximize efficiency.
Construction materials Ecological and Sustainable
Passive houses that prioritize the use of eco-friendly materials they are renewable, sustainable and respectful with the environment.
When we talk about passive houses, we can't ignore the importance of using construction materials ecological and sustainable . These materials not only contribute to reduce the environmental impact of the home, but also improve its energy efficiency and durability.
Wood: Excellent Insulation and Renewable
Wood is one of the most used materials in the construction of passive houses due to its many benefits. In the first place, is a material that is natural and renewable, which means that its production has an environmental impact much lower in comparison with materials such as concrete and steel. In addition, the wood has excellent insulating properties, which makes it an ideal choice for walls, ceilings and floors.
Another important aspect of the wood is its ability to regulate the indoor humidity. Thanks to their porous nature, the wood can absorb and release moisture depending on the environmental conditions, which helps to maintain a level of optimum moisture inside the housing. This not only improves the thermal comfort, but also contributes to a healthier environment for the occupants.
However, it is important to choose certified wood from sustainably managed forests. This ensures that the wood used in the construction does not contribute to deforestation or the deterioration of natural ecosystems.
Cork: Natural, Lightweight and Insulating Properties
The cork is another material that has gained popularity in the construction of passive houses due to its excellent insulating properties and its sustainable character. The cork is obtained from the bark of the cork oak, a tree that grows mainly in southern Europe and north Africa. The most interesting thing about this material is that it can be harvested without damaging the tree, making it an option is truly renewable.
In addition to its ability to thermally insulate, the cork also offers an excellent acoustic isolation. This makes it ideal for homes located in noisy areas or for people who value tranquility in your home. Another benefit of cork is its fire resistance and waterproof, which makes it a safe option and durable.
Straw-Ideal for Walls, due to its High Insulating Capacity
The straw is a material that is often overlooked in modern construction, but with a great potential in the context of passive houses. The straw is used mainly in the construction of walls thanks to its high insulating capacity, and low cost. In addition, it is an abundant resource and biodegradable, which makes it a sustainable option.
One of the biggest challenges of using straw in the construction is to make sure that you are well protected against moisture. If the straw gets wet, it may lose its insulating properties and begin to decompose. For this reason, it is usually combined with other materials, such as clay or lime, creating walls strong and durable.
Bioclimatic design and Orientation of the Housing
The bioclimatic design it is a key strategy in the construction of passive houses, as it seeks to adapt the home to the local climate to maximize your energy efficiency. This approach not only reduces energy consumption, but also improves the comfort of the occupants.
South, Maximizing Solar Gains in Winter
In the northern hemisphere, the orientation of the property plays a crucial role in the bioclimatic design. The main windows should be oriented to the south to capture the largest possible amount of sunlight during the cold months. During the winter, the sun low on the horizon, and goes straight for the south-facing windows, heating the home, the natural way.
However, in summer, the sun is higher in the sky and can get too hot if precautions are not taken. To avoid this, we use elements such as overhangs , awnings or even vegetation strategically placed to shade the windows. These elements act as natural barriers that block the sun excessive during the warmer months.
Cross ventilation: Design to Promote Air Circulation
Another important strategy in the bioclimatic design is the cross ventilation , that consists of designing the housing so that the air flows freely through it. This is achieved by placing windows and doors in opposite positions to create a flow of natural air. Cross-ventilation is especially useful in warm climates as it helps cool the home without the necessity of resorting to air-conditioning systems.
Adaptation to the Mediterranean Climate
One of the main advantages of passive houses is its ability to adapt to different climates. In Spain, where the mediterranean climate prevails in many regions, passive houses must be designed specifically to cope with hot summers and mild winters. This is achieved through strategies such as:
- Overhangs and awnings : To shade the windows during the warmer months.
- Cross ventilation : To cool the home naturally.
- Materials of high thermal mass : To absorb heat during the day and release it slowly during the night.
Home automation in Passive Houses
The integration of smart home automation systems in a passive house not only improves the energy efficiency, but also increases the comfort and convenience of the occupants. Home automation systems allow you to automate and control various aspects of the home, from lighting to air-conditioning, optimizing the use of energy.
The Intelligent Control of the Ventilation
One of the most common uses of home automation in passive houses is the intelligent control of the ventilation. Systems of controlled mechanical ventilation (VMC) can be programmed to automatically adjust the air flow speed according to the indoor air quality. For example, if the sensors detect an increase in the levels of CO2 or humidity, the system can increase the speed of ventilation to improve air quality.
Energy monitoring in Real-Time
Another important application of the automation is to monitor energy in real-time. Home automation systems can connect to power meters to provide detailed information on the energy consumption of the housing. This allows the occupants to identify patterns of consumption and make informed decisions to further reduce their carbon footprint.
Certification Passivhaus: Guarantee of efficiency and comfort
The certification Passivhaus is an international standard that ensures maximum energy efficiency and comfort in buildings. This seal of quality, which originated in Germany, has become a global benchmark for sustainable construction
Get the certification Passivhaus it is a rigorous process that ensures that the housing meets the most stringent standards of energy efficiency. This certification not only validates that the home is highly efficient, but also offers a guarantee of quality and sustainability. But, what does it mean exactly to obtain this certification?
The process begins with the design of housing, which should strictly adhere to the five core principles of the standard Passivhaus: thermal insulation , windows high performance , air tightness , controlled mechanical ventilation and utilization of solar energy . Each of these aspects must be carefully planned and executed in order to comply with the minimum requirements set by the Passivhaus Institut.
Key features
- Energy saving: Buildings certified can reduce up to 75% energy consumption compared with traditional buildings
- Superior comfort: Maintains a constant internal temperature and an optimum air quality
- Sustainability: Minimizes the environmental impact and contributes to the fight against climate change
Power Requirements
One of the most important requirements to obtain the certification Passivhaus is the energy consumption maximum allowed. According to the standard, a passive house should not consume more than 15 kWh/m2 per year for heating and cooling. In addition, the total primary energy consumption (including lighting, appliances, and other systems) should not exceed 120 kWh/m2 per year . These figures are extremely low in comparison with the conventional flats, which underscores the importance of careful design and high quality materials.
Leak tests
Another crucial step in the process of certification is the proof of tightness, known as Blower Door Test . During this test, place a fan in the front door of the house to create a pressure difference between the inside and the outside. This allows it to detect any leakage of air, and corrected before the home is finished. To comply with the standard Passivhaus, the rate of renewal of air must not exceed Of 0.6 air changes per hour at a pressure of 50 pascals. This level of waterproofing is essential to ensure that the home is highly efficient from the energy point of view.
Documentation and Monitoring
In addition to complying with the technical requirements, the certification process also includes extensive documentation and supervision by a certifier accredited by the Passivhaus Institut. This professional reviews all aspects of the design and construction of housing, from the initial plans to the installation of air-conditioning systems and ventilation. Continuous monitoring ensures that the housing meets the standards at each stage of the process.
The certification Passivhaus not only guarantees exceptional energy efficiency, but also increases the value of the property in the real estate market. Although the initial cost may be slightly higher, the investment is quickly recovered through the energy savings in the long term.
The process of building a Passive House
The construction of a passive house requires a meticulous approach and careful planning from the early stages of the project. Each phase of the process is crucial to ensure that the housing meets the strict standards of energy efficiency and comfort.
Design and planning
The design of a passive house begins with a detailed analysis of the site, including the solar orientation, the local climate and the characteristics of the terrain. Architects and designers use specialized software to model the thermal behavior of the housing and optimize every aspect of the design.
In this phase, take crucial decisions on the shape and orientation of the building, the location and size of the windows, and the interior layout. Each element is carefully considered to maximize the energy efficiency and comfort.
Material selection
The choice of materials is crucial in the construction of a passive house. Selected high quality material with excellent insulating properties and low thermal conductivity. Some of the commonly used materials include:
- Insulating, high performance, such as mineral wool, fiberglass or cellulose
- Windows triple glazing with frames for low thermal conductivity
- Membranes and tapes special to ensure the tightness
- Building materials with low carbon footprint
The selection of materials is not only based on its thermal performance, but also in its durability, sustainability and ability to contribute to an indoor environment healthy.
Construction and certification
The construction phase of a passive house requires a meticulous attention to detail and precise execution. The builders must be specially trained in the techniques and principles of building passive. Some key aspects during construction include:
- Careful installation of the insulation to prevent gaps or compression
- Sealed meticulous of all joints and penetrations to ensure the tightness
- Precision installation of windows and doors to eliminate thermal bridges
- Assembly and proper installation of the mechanical ventilation system
During and after the construction, carried out various tests and checks to ensure that the home meets the standards Passivhaus. These include:
- Tightness test (blower door test)
- Verification of the performance of the ventilation system
- Measurements of temperature and humidity
Once you have completed the construction and verified the compliance of all requirements, the housing can undergo the process of certification Passivhaus. This certification, awarded by the Passive House Institute, ensures that the housing meets the strict standards of energy efficiency and comfort.
Maintenance of a Passive House
Contrary to what you might think, the maintenance of a passive house is not more complicated than that of a conventional dwelling. In fact, in many aspects, it can be even more straightforward due to the high quality of the materials and systems used.
Is it more expensive to care for?
The maintenance of a passive house is usually not more expensive than that of a traditional home. Although the components and systems used are of high quality and can have an initial cost higher, durability, and long-term efficiency compensate for this initial investment.
The main aspects of maintenance in a passive house, which include:
- Cleaning and regular replacement of filters of the ventilation system
- Inspection and maintenance of seals and gaskets to keep the water tightness
- Care and cleaning of windows and doors high performance
- Periodic review of the system of heat recovery
Tips for maintaining energy efficiency
To maintain the energy efficiency of a passive house over time, the following practices are recommended:
- Perform regular maintenance of the ventilation system, including the cleaning or replacement of filters according to the manufacturer's recommendations.
- Periodically verify the integrity of the seals and gaskets to repair any damage that might compromise the waterproofing.
- Use solar protections (such as blinds, shutters or awnings) the right way to optimize solar gains, according to the station.
- To avoid modifications in the thermal envelope without consulting a professional who specializes in building passive.
- Educate occupants about the optimal functioning of the housing, including the proper use of ventilation and strategies for solar control.
How much does it cost to build a Passive House?
The cost of construction of a passive house can vary significantly depending on several factors. In general, it is estimated that the additional cost compared to a conventional home can range between 10% and 15%.
Factors that influence the cost
The cost of building a passive house can vary depending on several factors:
- Size of Housing: The size of the house is one of the main factors that influence the cost. The larger houses require more materials and workmanship, which can increase the total cost.
- Materials Used: The selected materials can also significantly affect the cost. The use of sustainable materials and high-quality can increase the initial price, but these materials tend to have a longer lifespan and require less maintenance in the long term.
- Complexity of the Design: The more complex designs may require more time and resources to its construction, which can increase the total cost. However, a design well planned can maximize the energy efficiency and reduce operating costs in the long term.
- Geographic Location: The cost of construction may vary depending on the region, due to differences in the costs of materials, labor, and local regulations.
- Certification Passivhaus: Even though you get the certification Passivhaus can slightly increase the initial cost, this cost is compensated for quickly with the term energy savings that provides the passive house.
Compared to a traditional home
Although the initial cost of a passive house can be higher than for a traditional home, it is important to consider the total cost of ownership in the long term. Significant savings in energy consumption, combined with lower maintenance cost and a longer performance life, can make a passive house is more economical over its useful life
Myths and facts about Passive Houses
Passive houses have generated much interest in recent years, but there have also been some myths around them. Let's look at some of the most common myths and the reality behind them:
Myth 1: The passive houses are much more expensive
Reality: while it is true that the construction of a passive house can be a initial cost is slightly higher, the difference is not as significant as you think. The costs usually range between 10% and 15% compared to a conventional home. In addition, this additional cost is offset rapidly with the energy saving, which can reach up to 75% compared to a traditional house.
Myth 2: The passive houses may not be cosmetically appealing
Reality: This is a myth is completely false. Passive houses can be so pretty and aesthetically pleasing as any other housing. The standard Passivhaus focuses on energy efficiency, but is not limited to architectural design. With a team of architects specialized, it is possible to design passive houses with big windows, innovative ways and in a variety of styles.
Myth 3: In a passive house does not need heating or air conditioning
Reality: Although passive houses are extremely efficient, they may require heating and cooling systems in certain climates. The difference lies in the fact that they need much less energy to maintain a comfortable temperature. The excellent insulation and water-resistance allow you to keep a stable temperature with minimal energy consumption.
Myth 4: you can't open the windows in a passive house
Reality: This is another common myth but fake. The windows in a passive house can be opened normally. The difference is that it is not necessary to open them to vent, because these homes have mechanical ventilation systems that renew the air constantly, by filtering and maintaining an optimal quality in the interior.
Myth 5: Anyone can design and build a passive house
Reality: Although any practitioner can be formed in the standard Passivhaus, the reality is that it requires specific knowledge and experience to design and build properly a passive house. It is important to have certified professionals who understand the principles and requirements of the standard to ensure its correct operation and certification.
FREQUENTLY ASKED QUESTIONS
What is a passive house?
A passive house, also known as Passivhaus, is a building designed and built under stringent standards of energy efficiency and thermal comfort. The main objective is to drastically reduce the power consumption, up to a 75-90% in comparison with a conventional dwelling, while maintaining an indoor environment comfortable all year round.
Key features:
– Design optimized to take advantage of passive solar energy,
– Thermal envelope is highly insulated
– Elimination of thermal bridges
– Air tightness exceptional
– Mechanical ventilation system with heat recovery
What is the Certification Passivhaus?
The certification Passivhaus is an international standard that ensures maximum energy efficiency and comfort in buildings. This seal of quality, which originated in Germany, has become a global benchmark for sustainable construction.
What are the main features of a passive house?
The main features of a passive house, which include:
- High level of thermal insulation: Used insulating materials of high quality and thickness superior to the conventional in walls, ceilings and floors.
- Mechanical ventilation with heat recovery: This system provides filtered fresh air constantly, recovering up to 90% of the heat from the outgoing air.
- Carpentry of high energy efficiency: It is used for doors and windows triple glazing with frames of low thermal conductivity.
- Air tightness: Creates a immersive underwater which prevents air infiltration, unwanted, verified by evidence of pressurization (blower door test).
- Solar orientation, optimal: The design makes the most of the solar radiation in winter and minimize it in summer.
- Elimination of thermal bridges: Special attention is given to the unions and meetings between building elements to prevent heat loss.
What are the benefits of living in a passive house?
Live in a passive house offers numerous benefits:
- Significant savings in the energy bill: The reduction of energy consumption can reach 90% in comparison with a conventional home.
- Greater thermal comfort: The interior temperature is stable, and pleasant throughout the year, without fluctuations abruptly.
- Better indoor air quality: Mechanical ventilation with filtration ensures a constant supply of fresh air, reduce allergies and respiratory problems.
- Reduction of the carbon footprint: The low power consumption translates into a significant reduction of CO2 emissions.
- Increase the value of the property: The certification Passivhaus energy efficiency and increase the value of the housing market.
- Less maintenance: The high quality of the materials and systems used reduces the need for long-term maintenance.
- Acoustic comfort: The excellent insulation also provides a significant reduction in exterior noise.
How much does it cost to build a passive house?
The cost of construction of a passive house can vary significantly depending on several factors:
- Location and local climate: The weather conditions may require different levels of insulation and design strategies.
- Size and complexity of the design: More designs simple and compact, they tend to be more economic.
- Quality of the materials and systems used: The choice of high quality components, you can increase the initial cost.
- Experience in the design and construction team: Teams with experience in building passive can optimize costs and processes.
In general, it is estimated that the additional cost compared to a conventional home can range between 5% and 15%. However, it is important to consider the total cost of ownership in the long term, since the savings in energy consumption and maintenance can make a passive house is more economical over its useful life.
How can reform a house to turn it into passive?
Yes, it is possible to reform an existing home to meet the standards, Passivhaus, although the feasibility and the cost will depend on the characteristics of the building. This process is known as "EnerPHit" and has criteria slightly less demanding than those of a passive house in new construction.
Key aspects of the reform:
- Improvement of the thermal insulation of the envelope
- Replacement of windows and doors with high-efficiency models
- Installation of a mechanical ventilation system with heat recovery
- Improving the air tightness
- Elimination of thermal bridges
The feasibility and the cost of the reform will depend on factors such as the age of the building, its conservation status and its architectural configuration.
How to vent a passive house?
The ventilation in a passive house is done through a mechanical ventilation system with heat recovery (MVHR, for its acronym in English). This system works in the following way:
- Extraction air: The exhaust air is extracted from the wet areas (kitchen, bathrooms), and major areas of occupation.
- Recovery heat: The extracted air passes through a heat exchanger, where it transfers its thermal energy to the fresh air coming in.
- Filtration: The fresh outside air is filtered to remove particles, pollen, and other pollutants.
- Distribution: The fresh air, preheating or precooling, is distributed to the rooms of the property.
This system ensures:
- A constant supply of fresh air and filtering
- Maintenance of the energy efficiency to recover up to 90% of the heat
- Control indoor humidity
- Elimination of odors and contaminants
The system MVHR works so smooth and quiet, ensuring an optimum indoor air quality without the need to open windows.
Can you open the windows in a passive house?
Yes, you can open the windows in a passive house. In fact, the ability to open the windows is a requirement of the standard Passivhaus to ensure the comfort of the occupants and provide additional ventilation when needed.
However, it is important to note that:
- The opening of frequent, windows it is not necessary to maintain a good indoor air quality, since the mechanical ventilation system is responsible for this.
- Open windows, for extended periods of time in extreme weather conditions can affect the energy efficiency of the housing.
- The mechanical ventilation system is designed to operate optimally with the windows closed, but it is flexible enough to adapt to the opening occasional window.
- In temperate climates, the opening of windows can be beneficial for the night cooling in the summer.
What materials are used in the construction of a passive house?
In the construction of a passive house using high-quality materials with excellent insulating properties and low thermal conductivity. Some of the commonly used materials include:
- Insulation:
- Mineral wool (rock or glass)
- Cellulose
- Expanded polystyrene (EPS) or extruded (XPS)
- Polyurethane
- Cork expanded
- Wood fiber
- Carpentry:
- Mark from high quality PVC
- Frames of wood or wood-aluminum
- Triple glazing with argon gas or krypton in the chambers
- Systems of waterproofing:
- Membranes and special tape to secure the seal to the air
- Structural materials:
- Wood (for dry building)
- Concrete (with additives to improve its thermal properties)
- Bricks and blocks, ceramic with low thermal conductivity
- Ventilation systems:
- Recuperator heat, high efficiency
- Ducts isolated
The selection of materials is not only based on its thermal performance, but also in its durability, sustainability and ability to contribute to an indoor environment healthy.
What is the difference between a passive house and a house with low energy consumption?
Although both concepts seek to reduce the energy consumption, there are significant differences:
- Efficiency standards:
- Passive house: Meet the strict criteria of the standard Passivhaus, which limits the demand for heating and cooling to 15 kWh/m2/year.
- House of low power consumption: Follow regulations less stringent, which vary by country or region.
- Power consumption:
- Home passive: Reduces energy consumption up to a 75-90% in comparison with a conventional home.
- House of low consumption: The reduction of the consumption is lower, usually between 30-50%.
- Water resistance:
- Passive house: Requires an air tightness exceptional, with a maximum of 0.6 air changes per hour at 50 Pa pressure.
- House of low consumption: The requirements of air tightness are less strict.
- Ventilation:
- Passive house: Use a mechanical ventilation system with heat recovery.
- House of low power consumption: Can use natural ventilation or simple mechanical systems.
- Thermal comfort:
- Passive house: it Ensures comfort and optimum temperature throughout the year without conventional systems of heating or cooling.
- House of low consumption: it May require conventional systems of air conditioning, although of less power.
- Certification:
- Passive house: Requires a specific certification (Passivhaus) with very strict criteria.
- House of low power consumption: Can have different certifications according to the local regulations or national.
Additional resources on Passive Houses
There are numerous sources of information about passive houses:
- Official organizations:
- Passivhaus Institut : passivehouse.com The official site of the Passivhaus Institut provides detailed information on the standard Passivhaus, including case studies, design tools, and educational resources.
- Construction platform Passivhaus (PEP) : plataforma-pep.org This Spanish platform to bring together professionals and experts in construction passive, offering resources and events related to the standard Passivhaus in Spain.
- Publications:
- Magazine of sustainable architecture and construction
- «Passive houses: Manual of design and construction» Wolfgang Feist
- «The passive house: a practical Guide to build efficient housing» various authors
- Events and conferences:
- International Passive House Conference
- Conferences and workshops organized by national associations
- Courses and training:
- Courses for design and construction of passive houses
- Certification programs for professionals
- Forums and online communities:
- Groups in social networks dedicated to building passive
- Forums specialized in sustainable architecture
- Videos and Documentaries : Search YouTube channels specializing in building passive, as Passivhaus TV or Green Building Council Spain that offer educational content and interviews with experts.
- Visits to passive houses:
- Open days organised by the owners or associations
- Demonstration projects in your area
- Contact with professionals:
- Architects and builders specializing in passive houses
- Energy consultants certified Passivhaus
- Design tools:
- Software PHPP (Passive House Planning Package)
- Databases of components certified Passivhaus
Remember that the most current and accurate information always comes from official sources and certified professionals in the standard Passivhaus.